Introduction
WordPress has become a household name in the world of website development. Known for its versatility and user-friendliness, WordPress powers millions of websites globally, from small blogs to large corporate sites. Whether you are a beginner looking to set up your first website or an experienced developer, understanding the ins and outs of WordPress can significantly enhance your online presence. This article provides a detailed guide to WordPress, covering its features, benefits, and practical tips for maximizing its potential.
What is WordPress?
WordPress is a powerful content management system (CMS) that allows users to create and manage websites with ease. Originally launched in 2003 as a blogging platform, it has evolved into a robust solution for building virtually any type of site, from e-commerce stores to portfolio websites. Its open-source nature means it’s continually being improved by a global community of developers.
Why Choose WordPress?
Benefits
One of the main advantages of WordPress is its flexibility. Whether you’re creating a simple blog or a complex website, WordPress provides the tools and features needed. It’s user-friendly, making it accessible for beginners while offering extensive customization options for advanced users.
Flexibility
WordPress supports thousands of themes and plugins, allowing you to tailor your site’s appearance and functionality to your needs. Themes control the design, while plugins add features like SEO optimization, social media integration, and more.
Community Support
With a vast community of users and developers, finding help and resources is straightforward. From forums to online tutorials, there’s a wealth of information available to help you troubleshoot issues and learn new skills.
Getting Started with WordPress
Choosing a Domain
Your domain name is your website’s address on the internet. It’s crucial to choose a name that is easy to remember, relevant to your content, and available. Domain registration services like Namecheap or GoDaddy can help you find and purchase your domain.
Selecting a Hosting Provider
Web hosting is where your website’s files are stored. Reliable hosting ensures your site is fast and accessible. Popular hosting providers for WordPress include Hostinger, Bluehost, SiteGround, and WP Engine, each offering different plans tailored to various needs.
Guide to choose best hosting provider hostinger vs Bluehost vs SiteGround vs WP Engine view full comparison.
Installing WordPress
Manual Installation
Manual installation involves downloading WordPress from its official site, uploading it to your server via FTP, and configuring it. This method offers a deeper understanding of the setup process but can be complex for beginners.
One-Click Installers
Many hosting providers offer one-click installers, simplifying the installation process. Services like Softaculous or Fantastico handle the setup for you, making it an ideal choice for those who want to get started quickly.
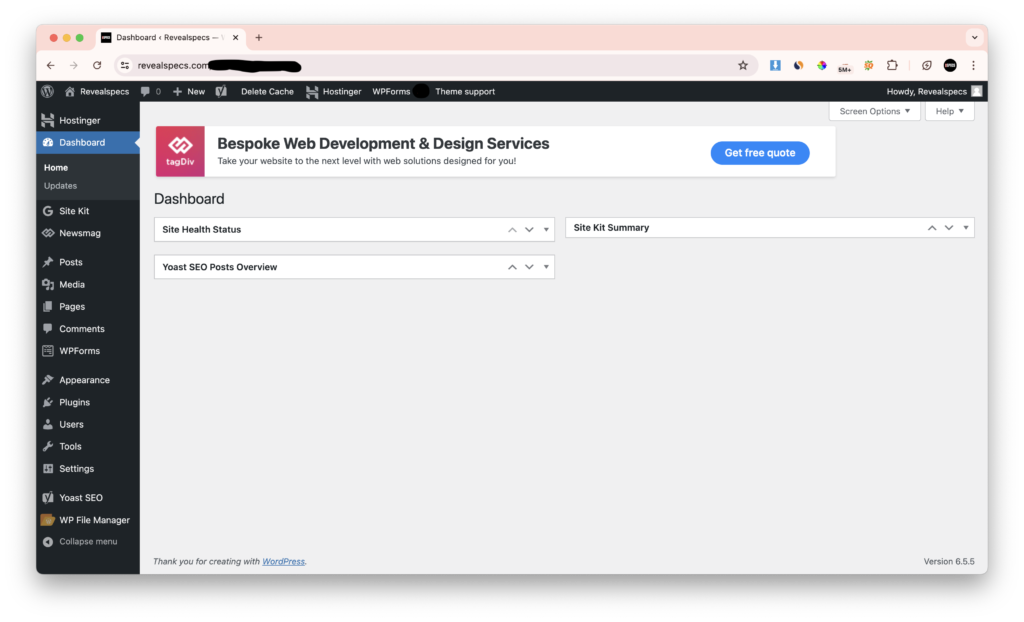
WordPress Dashboard
Navigating the Dashboard
The WordPress dashboard is your control center, where you manage all aspects of your site. From adding new posts to installing plugins, the dashboard is designed for intuitive navigation. Familiarizing yourself with its layout and features is the first step to effective site management.
Key Features
The dashboard includes sections for posts, media, pages, comments, appearance, plugins, users, tools, and settings. Each section serves a specific function, allowing you to customize and control your site comprehensively.
Themes and Customization
Selecting Themes
Themes dictate your site’s design. WordPress offers thousands of free and premium themes, each providing different layouts and features. Choose a theme that aligns with your site’s purpose and aesthetic.
Customizing Themes
Once you’ve selected a theme, you can customize it through the WordPress Customizer. This tool allows you to modify elements like colors, fonts, and layouts without touching code, making design changes accessible even to non-developers.
Child Themes
For more advanced customization, creating a child theme is recommended. A child theme inherits the functionality of the parent theme but allows you to make modifications without affecting the original theme files. This ensures your customizations aren’t lost during theme updates.
Plugins for WordPress
Essential Plugins
Plugins extend the functionality of your WordPress site. Essential plugins include Yoast SEO for search engine optimization, Akismet for spam protection, and WooCommerce for e-commerce capabilities.
Installing Plugins
Installing plugins is straightforward via the WordPress Plugin Directory. You can search for plugins directly from your dashboard, install, and activate them with a few clicks.
Managing Plugins
Regularly update and manage your plugins to ensure compatibility and security. Deactivate and delete any plugins that are no longer in use to keep your site running smoothly.
Creating Content
Posts vs. Pages
Understanding the difference between posts and pages is crucial. Posts are typically used for blog content and are displayed in reverse chronological order. Pages are static and ideal for content like About Us or Contact pages.
Using the Block Editor
WordPress’s Block Editor, also known as Gutenberg, Elementor allows for flexible content creation. Each piece of content (text, image, video) is a block that you can easily move, customize, and format.
Formatting Content
Well-formatted content improves readability and engagement. Use headings, bullet points, and short paragraphs to make your content easy to digest.
Media Management
Uploading Media
Adding images, videos, and other media to your site is simple with WordPress’s media uploader. Ensure your media files are high-quality and relevant to your content.
Organizing Media Library
Keep your media library organized by using descriptive file names and folders. This makes it easier to find and reuse media across your site.
Optimizing Images
Optimized images load faster, improving your site’s performance and user experience. Use plugins like Smush or ShortPixel to compress images without losing quality.
SEO Best Practices
On-Page SEO
On-page SEO involves optimizing individual pages to rank higher on search engines. Focus on keyword usage, meta title, meta descriptions, and internal linking to improve your SEO.
Using SEO Plugins
SEO plugins like Yoast SEO or All in One SEO Pack provide tools and recommendations for optimizing your site. These plugins help with tasks like generating sitemaps, adding meta tags, and analyzing content for keyword density (KD).
Creating SEO-Friendly Content
Create valuable, keyword-rich content that addresses your audience’s needs. Use clear headings, engaging introductions, and well-researched information to attract and retain visitors.
WordPress Security
Essential Security Practices
Securing your WordPress site is critical to protect against threats. Implement strong passwords, use two-factor authentication, and limit login attempts to enhance security.
Security Plugins
Security plugins like Wordfence or Sucuri offer comprehensive protection. These plugins provide features like malware scanning, firewall protection, and security notifications.
Regular Backups
Regular backups ensure you can restore your site in case of a failure or attack. Use plugins like UpdraftPlus or BackupBuddy to schedule automatic backups.
Performance Optimization
Speeding Up Your Site
A fast-loading site enhances user experience and improves SEO. Optimize your site’s speed by minimizing plugins (Maximum 13 – 16 plugin), optimizing images, and enabling browser caching.
Caching Plugins
Caching plugins like W3 Total Cache or WP Super Cache store a static version of your site, reducing server load and speeding up page load times.
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
CDNs like Cloudflare distribute your site’s content across multiple servers worldwide, ensuring faster access for users regardless of their location.
WordPress Maintenance
Updating WordPress
Regularly update WordPress core, themes, and plugins to benefit from the latest features and security patches. Keeping everything up-to-date reduces the risk of vulnerabilities.
Regular Site Audits
Perform regular site audits to identify and fix issues. Use tools like Google Analytics and Google Search Console to monitor site performance and troubleshoot problems.
E-commerce with WordPress
Setting Up WooCommerce
WooCommerce is the most popular e-commerce plugin for WordPress. It enables you to turn your site into a fully functional online store, complete with product listings, shopping cart, and checkout functionality.
Managing Products
Add and manage products easily with WooCommerce. You can categorize products, set prices, and manage inventory from the WordPress dashboard.
Payment Gateways
WooCommerce supports multiple payment gateways, including PayPal, Stripe, and credit card payments. Choose the gateways that best suit your business needs and configure them within WooCommerce.
WordPress for Blogging
Starting a Blog
Starting a blog on WordPress is straightforward. Choose a theme, set up your categories, and start writing posts. Regularly update your blog with fresh content to attract and engage readers.
Blogging Best Practices
Successful blogging involves more than just writing posts. Use compelling headlines, include images, and promote your posts on social media to reach a wider audience.
Engaging Your Audience
Engage your audience by responding to comments, asking questions, and creating interactive content. Building a community around your blog fosters loyalty and encourages repeat visits.
Advanced Customization
Using Custom Post Types
Custom post types allow you to create different types of content beyond standard posts and pages. Examples include portfolios, testimonials, and products.
Custom Fields
Custom fields enable you to add additional metadata to your posts and pages. Use plugins like Advanced Custom Fields to create and manage custom fields.
Theme Development
For those with coding skills, developing a custom theme provides ultimate control over your site’s design and functionality. Learn about WordPress’s template hierarchy and hooks to create custom themes.
WordPress Multisite
Setting Up a Multisite Network
WordPress Multisite allows you to run multiple sites from a single WordPress installation. It’s ideal for managing a network of blogs, company websites, or client sites.
Managing Multiple Sites
Multisite management involves overseeing themes, plugins, and users across all sites in the network. Use the network admin dashboard to streamline these tasks.
Migrating to WordPress
Migration Plugins
Migration plugins simplify the process of moving your site to WordPress. Popular options include Duplicator and All-in-One WP Migration, which handle the transfer of files and databases.
Manual Migration
Manual migration involves exporting content from your current platform and importing it into WordPress. This method requires more technical knowledge but offers greater control over the process.
Common Issues and Fixes
Migration can sometimes lead to issues like broken links or missing images. Use tools like Broken Link Checker to identify and fix these problems post-migration.
WordPress Community and Support
Forums
WordPress.org forums are a valuable resource for troubleshooting and learning. Engage with the community to ask questions, share knowledge, and find solutions.
Documentation
The official WordPress documentation (codex) provides comprehensive guides on all aspects of WordPress. It’s a go-to resource for both beginners and advanced users.
Professional Support Options
For more personalized help, consider hiring a WordPress expert or agency. Professional support can assist with custom development, site maintenance, and advanced troubleshooting.
Future of WordPress
Upcoming Features
WordPress continues to evolve with new features and updates. Stay informed about upcoming releases to take advantage of the latest improvements.
Trends and Developments
Trends like headless CMS, improved Gutenberg editor, and enhanced security measures are shaping the future of WordPress. Adopting these trends can keep your site modern and competitive.
FAQs
A: Choosing the right theme depends on your site’s purpose and your design preferences. Look for themes that are responsive, well-reviewed, and customizable.
A: Essential plugins include Yoast SEO, Akismet, Jetpack, and WooCommerce for e-commerce sites. These plugins enhance functionality and improve site performance.
A: Enhance security by using strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and installing security plugins like Wordfence or Sucuri. Regular backups are also crucial.
A: WordPress.com is a hosted platform that manages hosting for you, while WordPress.org is self-hosted, giving you more control over your site. Each has its own pros and cons depending on your needs.
A: Update WordPress, themes, and plugins as soon as new versions are released. Regular updates ensure you have the latest features and security patches.
A: Yes, WordPress is excellent for e-commerce when combined with WooCommerce. This plugin transforms your site into a fully functional online store.
Conclusion
WordPress remains the go-to platform for creating and managing websites due to its flexibility, extensive customization options, and robust community support. Whether you’re a novice or a seasoned developer, mastering WordPress can open up a world of possibilities for your online presence. By following the tips and best practices outlined in this guide, you can build a powerful, secure, and high-performing website that meets your goals and exceeds your expectations.














[…] vs WP Engine vs Bluehost Blogs What is CMS? A Beginner’s Guide Blogs WordPress: The Ultimate Guide Blogs How to Create a Google Developer Home Script Looping Until the Door is Closed […]
[…] What is CMS? A Beginner’s Guide Blogs WordPress: The Ultimate Guide Blogs How to Create a Google Developer Home Script Looping Until the Door is Closed […]